Fast fashion, a term often mentioned in discussions about fashion and the environment, refers to a model of clothing production and consumption characterized by speed and low cost. However, this rapid production and low pricing come with significant negative impacts on the environment, labor conditions, and society as a whole. To fully understand the effects of fast fashion, it is crucial to examine its manufacturing processes and consequences.
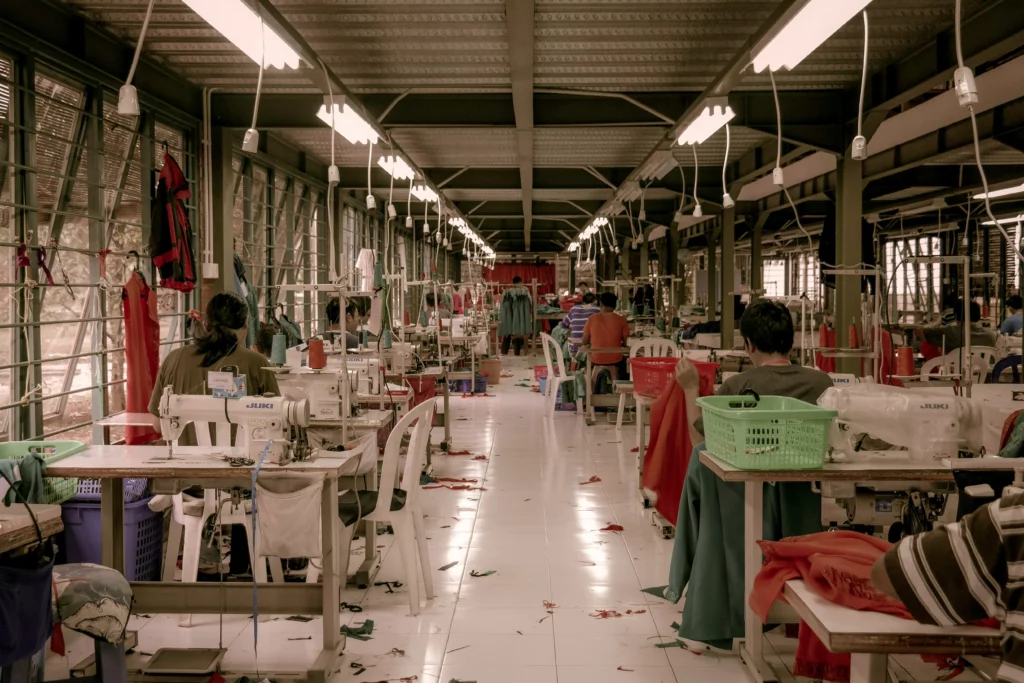

Fast fashion: production and consumption
Fast fashion relies on accelerated production methods that move designs from conception to sale in record time. To achieve this, brands use cheap materials and low-cost manufacturing processes. Production often takes place in countries with less strict environmental regulations and labor rights.
While this allows for low-cost clothing, it comes at the expense of quality and durability. The garments produced are often of poor quality and quickly become disposable.
Overconsumption and short garment life cycles
Fast fashion encourages overconsumption by constantly offering new collections at very low prices.
This abundance of choice pushes consumers to buy more than they need, creating very short clothing life cycles. Fast fashion items are often worn only a few times before being discarded. This type of consumption generates enormous amounts of textile waste.
Additionally, fleeting trends drive consumers to always chase the latest styles, further fueling this rapid consumption cycle.
Environmental and social impacts of fast fashion
Fast fashion has a devastating environmental impact. Massive clothing production requires large amounts of natural resources such as water and energy. For example, producing a single cotton T-shirt can require up to 2,700 liters of water.
Chemical treatments used to dye and process fabrics pollute waterways and soil. Synthetic fabrics like polyester release microplastics during washing, which eventually pollute oceans. Large amounts of textile waste often end up in landfills, where they take years to decompose, releasing toxic substances into the environment.
Labor conditions in the fast fashion industry are often precarious. Workers, primarily in developing countries, face long hours for very low pay in unsafe conditions. Human rights violations are common, including cases of forced labor and child labor.
Fast fashion brands outsource production to minimize costs, leading to a lack of accountability and transparency regarding working conditions in their supply chains.
Words from the Personal Shopper
Although fast fashion is attractive for its low prices and constantly updated trends, it poses significant problems for the environment and labor conditions. Accelerated production methods and the overconsumption it encourages generate massive waste and deplete natural resources. Workers’ conditions are often precarious and exploitative. Some brands also engage in greenwashing, so it is important not to be misled—learn more here.
It is crucial to recognize these impacts and seek more sustainable and ethical alternatives. By choosing eco-responsible brands and opting for high-quality, durable, and ethically made clothing, we can help reduce the negative impact of the fashion industry.
Younzee offers a solution with its virtual personal shopper and personal shopping app, helping you find clothing that fits your body and respects the environment, with a selection of women’s and men’s items from ethical and responsible fashion brands.
Transform your wardrobe with sustainable fashion pieces and take a step toward a more planet-friendly future by downloading the Younzee app on the Apple Store or Google Play.